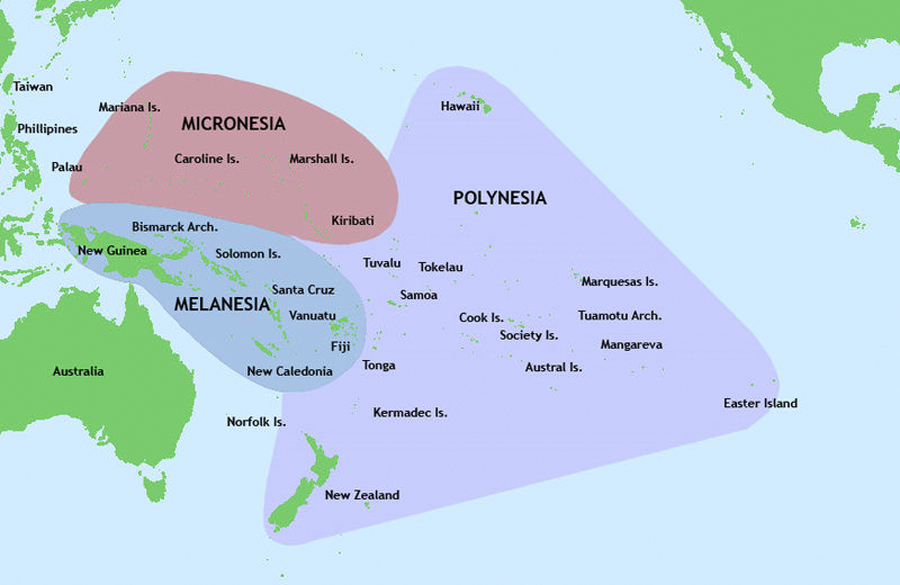
Micronesia, is a subregion of Oceania, comprising thousands of small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It is distinct from Melanesia to the south, and Polynesia to the east. The Philippines lie to the west, and Indonesia to the southwest.
The name Micronesia derives from the Greek "Mikros", meaning small, and "nesos", meaning island.
The following islands and groups of islands are considered part of Micronesia:
Caroline Islands, politically divided between Palau and the Federated States of Micronesia
Gilbert Islands, the main part of Kiribati
Mariana Islands, politically divided between the United States territories of Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands
Marshall Islands
Nauru
Wake Island, a United States Minor Outlying Island
Total land area: 1,229.95 square miles (3,185.6 km2)
Melanesia, is a subregion of Oceania extending from the western end of the Pacific Ocean to the Arafura Sea, and eastward to Fiji. The region comprises the countries of Vanuatu, the Solomon Islands, Fiji and Papua New Guinea; besides these independent countries, Melanesia also includes New Caledonia, a special collectivity of France, and the region of West Papua which is the location of two provinces of Indonesia, Papua and West Papua.
The name Melanesia derives from the Greek "Melas" meaning black and "nesos" meaning islands).
The following countries are considered part of Melanesia:
Fiji
Papua New Guinea
Solomon Islands
Vanuatu
Melanesia also includes one dependency of France: New Caledonia
Because the western half of the island of New Guinea is part of the nation state of Indonesia, Indonesia is also included in this area including the Maluku Islands and Raja Ampat Islands. Raja Ampat or the Four Kings, is an archipelago comprising over 1,500 small islands. Raja Ampat Regency is a new regency which separated from Sorong Regency in 2004.
Several Melanesian states are members of various intergovernmental organizations. Papua New Guinea, the Solomon Islands, and Vanuatu are members of the Commonwealth of Nations. Fiji, Papua New Guinea, Solomon Islands, and Vanuatu are also members of the Melanesian Spearhead Group.
Polynesia, is a subregion of Oceania, made up of over 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are termed Polynesians and they share many similar traits including language, culture and beliefs.[1] Historically, they were experienced sailors and used stars to navigate during the night.
The name Polynesia derives from the Greek "Poly" meaning many and "nesos" meaning island)
The following islands and groups of islands are considered part of Polynesia:
American Samoa (territory of the United States)
Cook Islands (self-governing state in free association with New Zealand)
Easter Island (called Rapa Nui in the Rapa Nui language, politically part of Chile)
French Polynesia (overseas country, a collectivity of France) Hawaii (a state of the United States)
New Zealand (independent nation)
Pitcairn Islands (a British Overseas Territory)
Samoa (independent nation)
Tonga (independent nation)
Tuvalu (independent nation)
Wallis and Futuna (collectivity of France)
Rotuma (Fijian dependency)